5 Ways That Pricing Externalities Supports the Transition to a Circular Economy
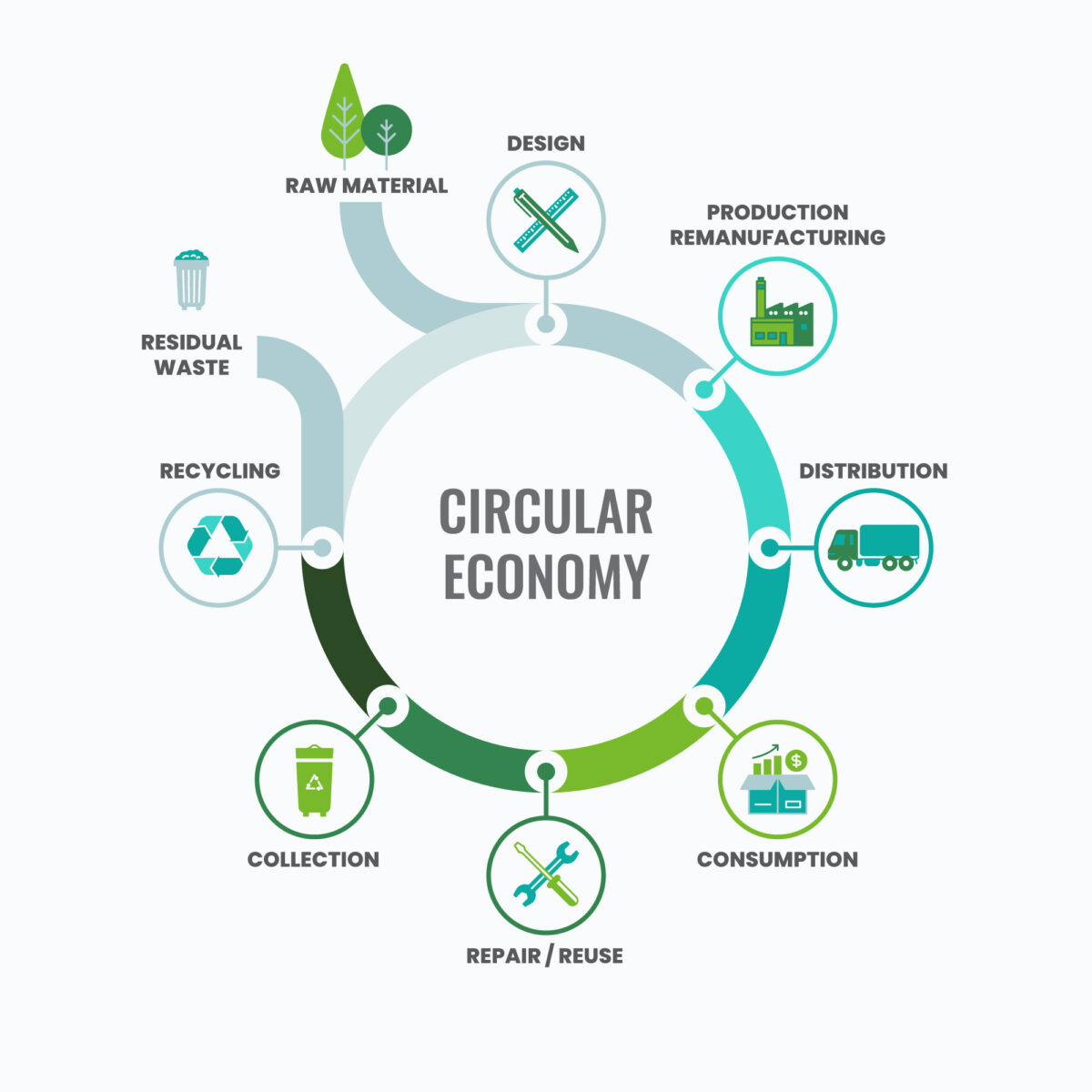
A circular economy aims to minimize waste and resource depletion by designing products, materials, and systems that enable reuse, repair, remanufacturing and regeneration. Pricing externalities is a key mechanism that can support the transition to a circular economy.
Externalities refer to the costs or benefits of economic activities that are not reflected in the prices of goods or services. In the context of a circular economy, externalities often arise from the negative environmental impacts associated with resource extraction, production, consumption, and waste disposal. These impacts, such as pollution, resource depletion, and greenhouse gas emissions, are typically not accounted for in market prices.
By pricing externalities, the true costs of resource use and waste generation can be internalized into the economic system ensuring the environmental costs associated with the production and consumption of goods and services are included in their market prices, creating economic incentives for more sustainable and circular practices.
Below are 5 ways that pricing externalities can support the transition to a circular economy:
1. Fosters innovation and technological development: Pricing externalities encourages the development of new technologies, processes, and business models that minimize waste and resource use. A linear model is driven by volume and consumption to generate revenue, and everyone wants more revenue. Circular business models are driven by value and performance offering revenue without volume throughput e.g. lighting as a service, air-conditioning as a service, even Boeing charging by the mile rather than selling engines to airlines.
2. Encourages resource efficiency: When the environmental costs of resource extraction and depletion are factored into prices, businesses and consumers are motivated to use resources more efficiently. This can decrease waste generation, increase repurpose, repair, and reuse with recycling only as a last resort relieving pressure on extraction of finite resources.
3. Promotes eco-design and sustainable production: By pricing externalities, the costs of pollution and environmental degradation caused by production processes can be incorporated into prices making it much more likely that businesses adopt cleaner and more sustainable production methods, invest in eco-design, and develop products that are easier to repair, upgrade, and recycle.
4. Supports the circular supply chain: Pricing externalities can drive changes throughout the entire supply chain. Suppliers and manufacturers are encouraged to adopt circular practices, such as using the waste and energy streams of adjacent businesses, incorporating recycled materials into new products, implementing closed-loop systems, and optimizing logistics to reduce waste and emissions.
5. Shifts consumer behaviour: When the true environmental costs are reflected in prices, many consumers are more likely to make informed and sustainable choices or choose to reduce overall consumption.
Ready to Explore More of the power of the Planet Price Platform?
Request a demo or a Scope 3 Tread Lightly Assessment



